Adding external content (YouTube, etc.)
This resource covers how to access and usesuitable content from sites such as YouTube, TED, and Twitter in your teaching. It provides options for how to embed this content within the relevant context of your Moodle site.
Why?
There are many potential reasons to embed external content into your subject site. These will vary depending on your context. For example, in a journalism subject, it can be difficult to teach about the decentralisation and democratisation of journalism without relevant examples from sources such as Twitter and YouTube. You may be aware of an effective short video on TED.com where the speaker introduces the week’s content perfectly. Once you have checked the clip's appropriate authorship, copyright and sharing rights, you can embed it into your site, providing rich multimodal content for your students.
It is crucial to consider the quality of the resources embedded in your content, consider:
What is its purpose?
The resources you use should be appropriate for the context where they will be embedded. Some helpful questions to ask include:
- What is the purpose of the content?
- Does it provide clarity?
- Does it show a contrary opinion or alternate viewpoint?
- Does it add additional data?
Is the content from a reputable & reliable source?
When adding external content, there is an inherent risk that the resource may be removed at any time, and you may not know this until you use it. To mitigate these risks, prefer content from reputable sources. Consider the following questions:- Are the author and the uploader of the content the same?
- Does it pass the CRAAP test?
In the example below, the BBC Earth channel has uploaded a clip from a BBC nature documentary. This source is considered reputable, and the video is unlikely to have copyright issues.
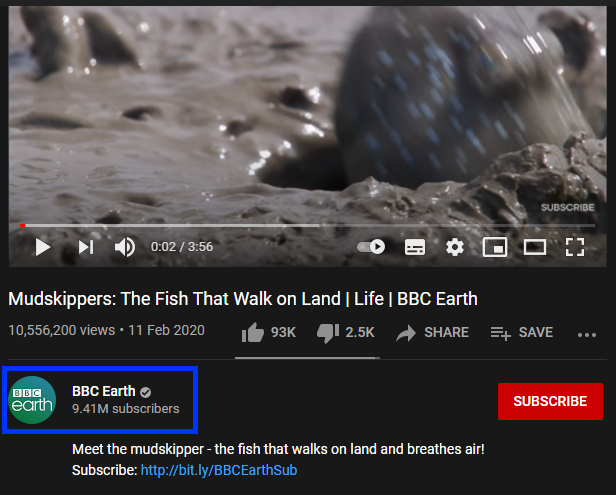
The same video uploaded to an individual's YouTube channel has a much higher risk profile for copyright infringement. You should avoid resources where the authorship and uploader are inconsistent.
When using external resources in your teaching, always adhere to the guidance in the UOW Library resource Copyright guidance for teaching staff.
How?
When adding external resources to your site, think about how your design choices will affect students' experience. For example, if you embed a video on the main page, will students need to watch it (and therefore load it) every time they log in? Is this necessary, or could it negatively impact their experience? Would it be more effective to place the video in a different section, such as a separate page or activity, where it might be more relevant and less intrusive?
Adding content to your subject site
- Ensure Edit mode is on.
- Navigate your Subject site to where you want to embed the external content.
- Using the Atto editor, click Show/hide advanced and click the HTML icon (viewed as </>).

- Paste the HTML code from your clipboard. The code will look like this:
<iframe width="1280" height="720" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/BtN-goy9VOY" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>Many content hosting platforms (e.g. YouTube, Vimeo, and Twitter) make it easy to find the HTML embed code. More information about sourcing the embed code is available in the section below. - Add the relevant Copyright Notices.
- Click the Save and display button.
Sourcing the HTML embed code
Many sites that host content that you might consider embedding into your subject site have built-in sharing and embedding functionality. Where possible, use these as they are designed to maximise the compatibility of the content being embedded.
- Youtube - Embed videos and playlists
- TED - uses the YouTube player, and by extension the same process as YouTube above.
- X (formerly Twitter) - Embed a post- Note: This allows you to customise and preview the embed code.



